Learn about the growing importance of AIs in voice search marketing and how to sell more through voice searches.

Voice searches are an information search mode that has entered overwhelmingly into people's daily lives. According to Google reports, already 27 percent of the world's population uses voice searches on mobile devices.
There is no need to hide behind a finger. Voice search marketing is the future, in fact, it is the present!
Why are voice searches catching on (and can't we do without them)?
First of all, let's clarify what we are talking about. Voice search (voice search) is a technology that implements voice recognition and allows you to perform online searches without the need to type text into the search engine, but simply by voicing what you need.
The device's voice assistant (Google Assistant, Alexa, Cortana, Siri) to which one expresses the search interprets the question formulated and provides the results deemed relevant.

Clearly, this is an information search mode that is used exclusively (or almost exclusively) on smartphones. Voice assistants, on the strength of a language understanding technique implemented with advanced machine learning techniques, save time and express complex, discursive searches.
Conducting searches with voice is definitely intuitive and within everyone's reach. Even though text-to-voice technologies to date are not yet perfect, they are equally useful tools that are relevant to everyone's life. Let's think about this for a moment. Search engines are tasked with returning resources that come as close as possible to the queries expressed by users. If such queries (searches performed online) are now expressed verbally, in much more varied ways than they used to be, the results provided by Google & co. will also have to change to match this new paradigm. Which means that all those who also sell through Google will have to follow the evolution of these mechanisms with interest.
According to a study presented by Google:
- 40% use voice search to ask for directions.
- 39% use the feature to dictate a text message.
- 32% do so to make a phone call.
- 23% of U.S. adults use voice search "when I'm cooking."
- 51% of teens (and 32% of adults) use voice search "just for fun."
- 27% use voice search to check the weather.

Are voice assistants helping us or spying on us?
Artificial intelligence is now advanced enough to interpret the meaning of users' searches and return answers relevant to what is requested. All we need to do is to address the device's voice assistant with the right expression ("Hey Google," "Hey Siri," etc.) and state the question so that our virtual friend will either read to us or present the desired answer on the screen.

But on balance, if our phones are constantly listening to what we say, are we completely deprived of privacy? Not exactly so. Clearly, devices must be able to hear what is being said nearby in order to activate on command, but there is a "barrier to entry" that is deactivated upon receipt of the appropriate formula. In the absence of this, it receives but does not interpret what is being said. This limitation is deactivated when we send the vocal assistant the appropriate command: the device then enters the mode of interpreting the sounds it picks up in order to provide a response to the commands given. Of course, it can also happen that the assistant activates when we say "Hey Google" or "Hey Siri" as part of a speech, but that is another matter!
Voice search marketing: how it is changing the marketplace
Voice marketing is a web marketing strategy that appears indispensable for companies operating online.
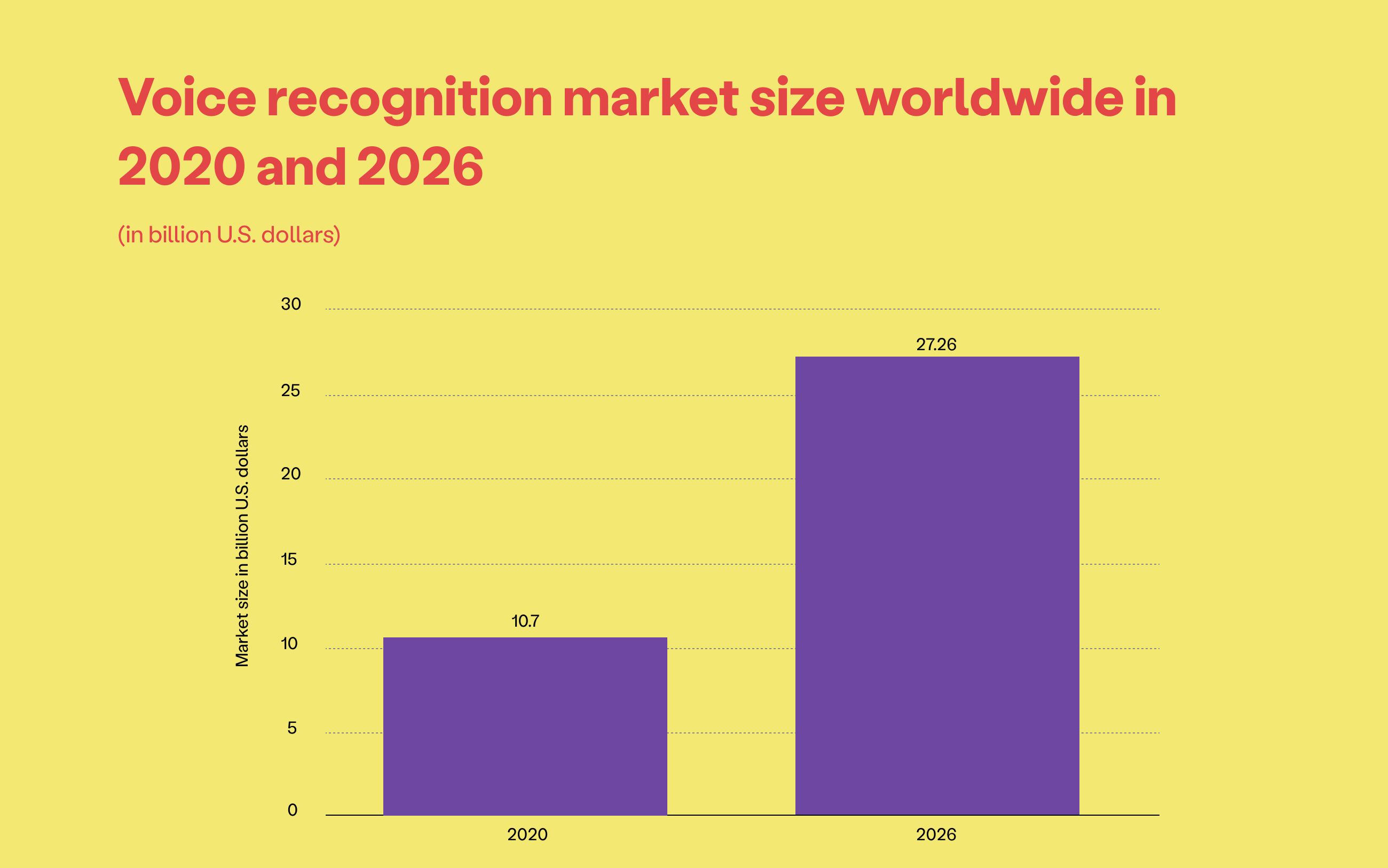
According to a statista report, the voice recognition market will grow from $10.7 billion by 2020 to $27.16 billion in 2026. This is not simply an extension of common online search activities, but a real revolution in the online marketplace.
Another interesting key takeaway from an SEO perspective is that searches performed by voice tend to be articulated and posed in an informal tone, a consistent departure from the classic paradigm of typing in preset formulas (such as those suggested by Google Suggest). People, especially the younger generation, boast an awareness of the immense possibilities made available by these recent technologies.
Each person can make use of different expressions and idioms to define the products and services they need. Long-tail keywords are just the "building blocks" of long and complex formulas that people have every interest in using to find solutions that better meet their needs. Using a language and tone of voice that is less technical/formal and closer to those that your users use can prove to be a winning strategy. Similarly, leveraging UGC (User Generated Content) in the context of product reviews can create high relevancy between queries and content on the landing page.
Brands can use voice technologies to promote many types of products and services. As Google reports, 51 percent of people 55 and older like to formulate voice searches since this allows them to get instant answers.
Voice assistants are becoming more advanced every day and better able to interact with a variety of languages and expressive formulas. How can we benefit from this trend through artificial intelligence?
Voice Marketing Strategies with AI
SEO optimization for AI assistants, which are gaining a foothold on an increasing number of devices not originally designed to conduct research, requires a certain amount of specialized expertise to take full advantage of this trend.
Artificial intelligences make it possible to set up customer care systems that allow, for example through chatbots on the site, to follow up on potential customers' inquiries, provide them with information or direct them to appropriate operators.
With automated systems, feedback can be obtained that can in turn improve the service provided, make it easier to retain customers, reduce the time needed to perform tasks, and increase the time available to perform more productive tasks.

Web content can be rethought to respond more stringently to verbally expressed queries. Introducing speech recognition technology into their apps can help marketers better understand what people are looking for and what they expect from products.
Google Business Profile tabs are essential tools for responding to searches for local stores and businesses near people who utter searches peppered with "near me." So remember to provide as much information as possible to make your GBP tab relevant to local searches voiced by voice. Address, phone number, opening hours, closing days, services offered, etc.

Creating SEO-oriented content designed to address specific local search needs is a good way to increase a portal's visibility for a specific geographic area. In this way, physical stores related to ecommerce can devise effective drive-to-store strategies to increase visits and consequently sales, starting with online content. Demandsage reports that about 58 percent of customers use voice searches to find a local business.
Structured data is an important configuration for increasing the ability of search engines to interpret the information provided by websites. With this data, one can optimize the content of a portal by making it more easily understood by search engines, and create more relevant results in serp, consequently increasing organic traffic from targeted users. With structured data, it is also possible to contextualize FAQs, found in various locations on the site, in order to help search engines more easily identify answers to possible questions expressed verbally.
As we have seen, people's online search habits are changing dramatically. Artificial intelligence can help brands create content that responds to voice searches such as information about activities in the area, answers to frequently asked questions, extrapolate long tail keywords from which to create human friendly texts. We don't have to delegate the entire creative process to automated tools like ChatGPT, as much as use them intelligently to optimize the time needed in content creation, freeing up resources to devote to the steps that can really make a difference.
