Find out everything you need to know about the Stanca Act and why you need to ensure digital accessibility of websites.


Index
- What is the Stanca Act
- Who will be obliged to comply with the requirements of the Stanca Act.
- The importance of digital accessibility
- What are the WCAG Guidelines and what are the accessibility principles required for private companies?
- The benefits of an accessible website for users and businesses
- How to improve digital accessibility: inclusive design
- Does web accessibility help a website's SEO ranking?
- Accessibility and websites: conclusions
Digital accessibility has become an increasingly relevant issue in today's society, in which the use of digital devices and access to online content is now an integral part of daily life. The Stanca Act, officially known as Law 4 of 2004, is an Italian law that deals precisely with promoting the accessibility of websites and digital applications. In this article, we will explore in detail the Stanca Act and the importance of digital accessibility that it enshrines.
What is the Stanca Act
The Stanca Act is named after then-Minister of Innovation and Technology Lucio Stanca, the promoter of this important legislation. Passed in 2004, the Stanca Act aims to make websites and digital applications accessible to all people, including those with disabilities. This law is a fundamental tool for ensuring the inclusion of all users and promoting a web that is accessible and usable by anyone.
Who will be obliged to comply with the requirements of the Stanca Act.
Those who must comply with the requirements of the Stanca Act include, in addition to public administrations (thus schools, regions, provinces, municipalities, universities, etc.):
- public economic entities
- private companies that have a concession to provide public services
- the regional municipal companies
- the public welfare and rehabilitation agencies
- the transportation and telecommunications companies in which public capital prevails
- companies that provide information technology services to public entities through contracts
- all entities that receive public grants or subsidies to deliver their services through information systems or the Internet.

The importance of digital accessibility
The Stanca Act recognizes and protects the right of access of citizens with disabilities to computer and telematic services offered by the public administration, guaranteeing full compliance with the fundamental principle of equal opportunity and ensuring accessibility to public administration services for people with disabilities.
Digital accessibility is essential to enable all people to access and use digital content without barriers. This is especially relevant for people with disabilities, who may have difficulty using websites or applications that are not accessible. In addition, digital accessibility also benefits users without disabilities by improving usability and the overall experience.
What are the WCAG Guidelines and what are the accessibility principles required for private companies?
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 2.1 (WCAG) are a list of recommendations designed to improve the accessibility of Web content.
By adopting these guidelines, content can be made accessible to more people with various disabilities, including:
- blindness and low vision
- deafness and hearing loss
- motor limitations
- speech disabilities
- photosensitivity
- and combinations of these conditions.
WCAG 2.1 applies to desktop, laptop, tablet and mobile devices.
The benefits of an accessible website for users and businesses
An accessible website offers benefits for both users and the businesses themselves. In fact, for businesses, digital accessibility offers several opportunities:
- Expansion of user audiences: an accessible website or application can be used by a wider audience, including those who have disabilities or difficulties in accessing digital content.
- Improved corporate image: showing a commitment to digital accessibility can improve a company's image and reputation. This demonstrates a focus on the needs of all users and inclusion as a corporate value.
- Improved user experience: the natural consequence of adopting WCAG principles is improved user experience (UX) and navigation paths. The consequence of improved web project navigation is obviously improved conversion rates.
Not bad, right?

How to improve digital accessibility: inclusive design
Improving digital accessibility requires inclusive design from the initial stages of development, and this design method is based on the concept of "design for all," which aims to create products and services that are accessible to all people, regardless of their abilities or disabilities.
Designing a website with accessibility in mind is certainly a challenge, but it is definitely a more efficient process than optimizing a pre-existing web design.
Below I try to summarize what the best practices are for effective inclusive design:
- Know the guidelines: first of all, you need to know what you are doing because the Accessibility Statement (which will be mandatory to include in the footer of the website) is a document that requires some bureaucratic steps that are not obvious.
- Use accessible technologies: choose development technologies that support accessibility, such as responsive design templates, semantic code, alternative text for images, and intuitive navigation controls.
- Color contrast: make sure the colors used are sufficiently contrasting to allow the text to be clearly readable for people with visual impairments.
- Testing with diverse users: it is important to involve users with disabilities in the testing process to assess the actual usability of the product. This will provide you with valuable feedback and allow you to identify any accessibility issues that cannot be identified by automated software.
- Keyboard navigation: it is also critical to ensure that all features of the web project are accessible via keyboard, allowing users with mobility disabilities to navigate and interact without the use of a mouse.
- Alternative text and descriptions: alternative text (alt tag) for images is not an SEO attribute as many people think, but was created for the purpose of making users with visual disabilities understand the content of images through screen readers or other assistive technologies. It is therefore not an area for keyword stuffing.
- Clear semantic structure: using a well-organized structure for content and respecting header hierarchies makes it easier for users with disabilities to understand and navigate content. I realize it is quicker to use the H2 tag in Call to Action because it usually uses a* larger font, but it is not the correct way to semantically structure web content. The asterisk was born out of a disquisition with our creative director Paolo Orsacchini, and not having found a solution to the dilemma we decided to make "font" gender free.
- Accessible formats: you will need to provide alternatives to non-accessible file formats (such as non-text PDF documents) by offering text versions or documents that are structured in an accessible way.
Does web accessibility help a website's SEO ranking?
You may be wondering: does making a website accessible have any impact on a web project's SEO performance? The answer is yes, and I will try to briefly explain why with simple logical reasoning.
But let's start with the basics.
Our mission is to organize information from around the world and make it globally accessible and useful.
This is Google's mission, and although by "accessible" it means usable, going through some of the documents on Google Search Central it is easy to see how accessibility and User Experience are intertwined.
In May 2020 Google announced two new ranking algorithm updates, "Google Page Experience Update" and "Core Web Vitals." The focus of these two updates was the introduction of a set of metrics that evaluate the User Experience of a website and deemed essential for a good user experience and a more enjoyable web. These two updates went into rollout between June 2022 and March 2022 and affected Google's SERPs (Search Result Pages) in no small way.
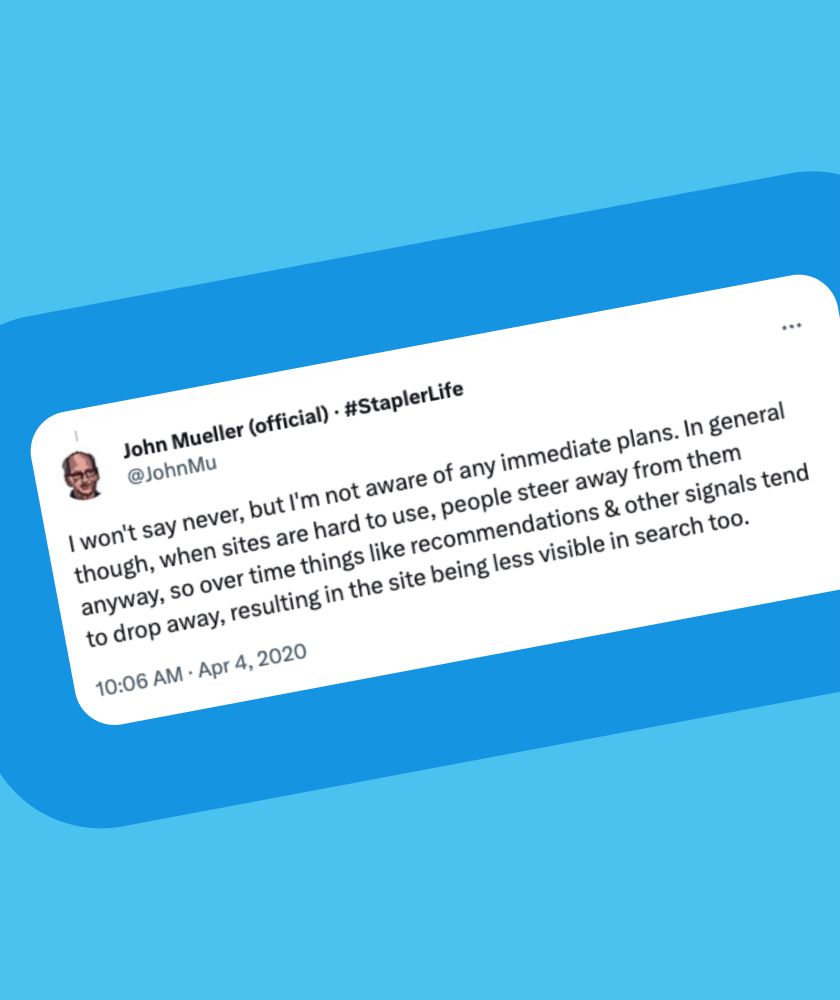
Also corroborating this claim is a 2020 tweet by John Mueller, Google's Search Advocate, which I translate for simplicity: "Never say never, but I'm not aware of any immediate plans (to make accessibility a ranking factor, ed.). In general, though, when sites are difficult to use, people turn away from them anyway, so over time recommendations and other signals tend to diminish, resulting in the site being less visible in searches as well."
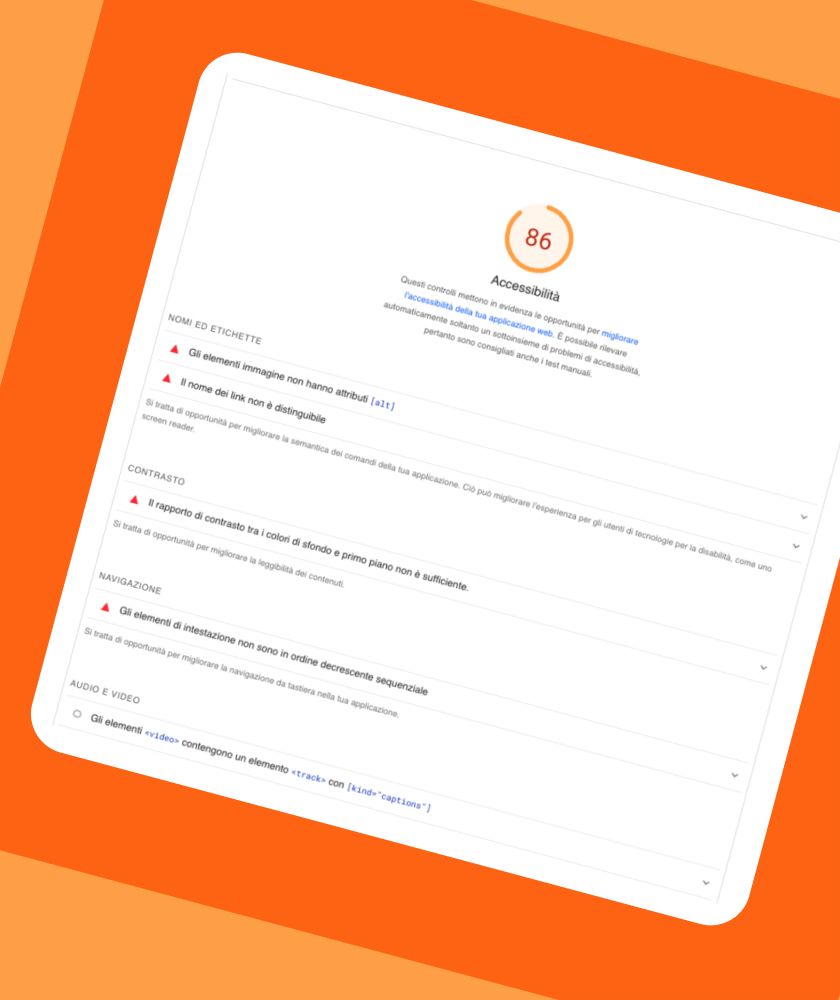
A very important tool at our disposal that allows us to get an idea of the accessibility of pages is Google Lighthouse.
Google Lighthouse is an open source tool that allows us to evaluate the quality of web pages from the point of view of loading speed and browsing experience. This platform offers usability considerations of a website divided into five areas of analysis: Performance, Best Practices, Accessibility, SEO, and Progressive web Apps. We can use it to identify areas of visual and functionality improvements on which to intervene to make a portal more user-friendly.
Accessibility and websites: conclusions
So, to recap:
- Google mentions accessibility in its mission statement.
- Two updates were released in 2022 that reward websites with an optimal user (and browsing) experience
- Within Google's official documentation on usability, two important points are mentioned: 1) How easy is it for visitors to reach or locate the main content of the pages? 2) Is the page designed so that visitors can easily distinguish the main content from the less important content?
- John Mueller corroborates the above theses by stating, logically, that difficult-to-navigate websites will suffer a drop in ranking
- Lighthouse is a useful tool to analyze site performance and find out in which areas it is convenient to take action to improve accessibility.
Summing up a bit, we can say with a sufficient degree of certainty that making a website accessible is not a direct but a derivative ranking factor, as it is closely related to the concept of User Experience. Furthermore, improving the navigability of a website by adopting WCAG principles can affect conversion rates and user retention, all positive signals that search engines take into account when evaluating the relevance of a search result to a specific query.
The Stanca Act represents an important step in ensuring digital accessibility in Italy. Digital accessibility is key to enabling all people to access and use digital content without barriers, promoting inclusion and autonomy. Improving digital accessibility offers many benefits to users and businesses, creating a more accessible and usable Web for all.
